On-page SEO techniques include optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, and headers with relevant keywords, ensuring proper URL structures, and maintaining high-quality, original content. Focus on internal linking and image optimization with alt tags. Enhance page speed, mobile-friendliness, and user experience for better rankings.
Introduction
On-Page SEO Techniques (search engine optimization) is vital because it lays the foundation for your website’s visibility on search engines. By optimizing these elements, you ensure search engines can effectively crawl, index, and understand your content, leading to better rankings and increased organic traffic,in VM IT SOLUTION, Best SEO Agency in Chennai.
On-page SEO, also known as on-page SEO, refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) and attract relevant traffic. It focuses on improving both the content and the HTML source code of a page. Unlike off-page SEO, which involves external factors like backlinks, On-Page SEO Techniques is entirely within the webmaster’s control.
What is Search Engine Optimization?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of enhancing a website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) to drive more organic (non-paid) traffic. It involves implementing strategies and techniques to improve a website’s ranking for specific keywords or phrases that users search for on platforms like Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
SEO focuses on understanding how search engines work, what users are searching for, and how to provide the best content to meet those needs.
Core Components of SEO
On-Page SEO:
Optimizing elements on your website, such as content, meta tags, headings, images, and URLs, to make it search-engine-friendly.
Off-Page SEO:
Building the website’s authority and trustworthiness through external strategies like backlink building, social media promotion, and influencer outreach.
Technical SEO:
Improving the technical aspects of a website, such as site speed, mobile-friendliness, secure connections (HTTPS), and XML sitemaps, to enhance crawlability and indexing.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO Techniques (also known as on-site SEO) is the process of optimizing individual web pages to improve their rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs) and attract more relevant traffic. Unlike off-page SEO, which focuses on external factors like backlinks, On-Page SEO Techniques deals with the elements of your website that you can control, such as content, structure, and HTML source code.
On-Page SEO Techniques ensures that search engines can understand your content effectively and that users have a seamless and engaging experience.
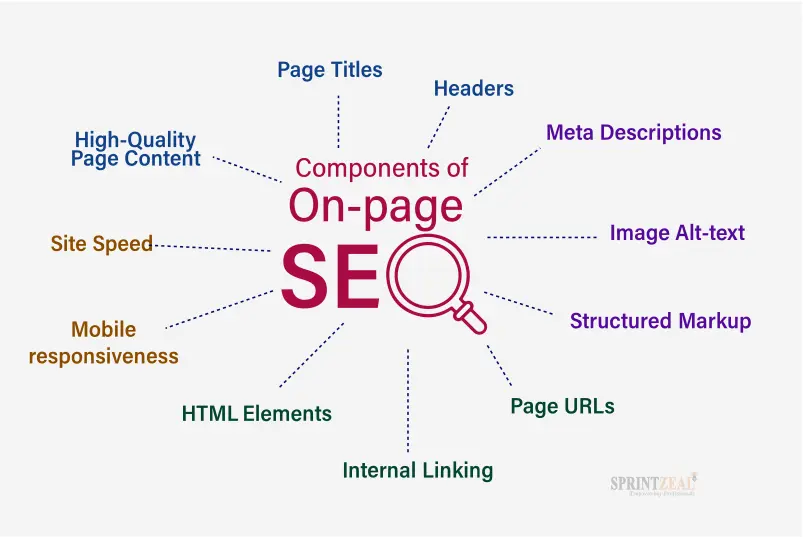
Key Elements of On-Page SEO
- High-Quality Content
- Content is the foundation of on-page SEO.
- It should be relevant, informative, and engaging, catering to the needs and intent of your target audience.
- Use primary and secondary keywords naturally without overstuffing.
- Keyword Optimization
- Perform keyword research to identify terms your audience is searching for.
- Include keywords in strategic locations such as:
- Title tags
- Headings (H1, H2, etc.)
- First 100 words of the content
- Meta descriptions
- Image alt text
- URLs
- Title Tags
- The title tag is one of the most important on-page ranking factors.
- Create compelling, keyword-rich titles under 60 characters to ensure they display correctly in SERPs.
- Meta Descriptions
- A brief summary (under 160 characters) of the page’s content.
- Though not a direct ranking factor, a well-written meta description improves click-through rates (CTR).
- Headings and Subheadings
- Organize content with structured headings (H1, H2, H3).
- Use keywords in headings to signal relevance to search engines and improve readability.
- URL Structure
- Use clean, descriptive, and keyword-rich URLs.
- Avoid long URLs with unnecessary characters or numbers.
- Internal Linking
- Link to other relevant pages on your website to:
- Improve navigation.
- Help search engines discover more pages.
- Enhance user engagement.
- Link to other relevant pages on your website to:
- Image Optimization
- Compress images to reduce file size and improve load speed.
- Use descriptive file names and alt tags with keywords for accessibility and SEO.
- Page Speed
- Ensure fast loading times by optimizing code, images, and server response.
- Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can help identify issues.
- Mobile-Friendliness
- Your website must be responsive and provide an optimal experience on all devices.
- Mobile usability is a significant ranking factor.
- User Experience (UX)
- Create an intuitive and engaging website design.
- Ensure easy navigation, fast load times, and high-quality content to keep users on the page longer.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup)
- Implement structured data to provide search engines with additional context about your content.
- This can enhance rich snippets, such as reviews, FAQs, or product information.
- Canonical Tags
- Use canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues and guide search engines to the preferred version of a page.
Why is On-Page SEO Techniques Important?
On-Page SEO Techniques is critical because it lays the foundation for how search engines and users perceive your website. It directly impacts your website’s ability to rank in search engine results pages (SERPs), attract relevant traffic, and provide a seamless user experience.
Here are the key reasons why On-Page SEO Techniques is important:
1. Improves Search Engine Rankings
On-Page SEO Techniques helps search engines understand the content and context of your web pages. When your page is properly optimized with targeted keywords, structured headings, and other SEO-friendly elements, it signals relevance to search engines.
- Search engines like Google reward well-optimized pages with higher rankings.
- The higher your ranking, the more visibility your page gets.
2. Increases Organic Traffic
By optimizing individual web pages for specific keywords, On-Page SEO Techniques ensures your content appears in front of the right audience. This drives organic traffic—visitors who find your website through unpaid search results.
- Higher rankings for relevant searches result in more clicks and visits to your website.
- Organic traffic is a sustainable and cost-effective source of website visitors.
3. Enhances User Experience (UX)
On-Page SEO Techniques is not just for search engines; it’s also for your users.
- Optimized content provides value by answering users’ questions clearly and comprehensively.
- Factors like fast loading times, mobile-friendly design, and easy navigation improve the user experience.
- A positive experience keeps visitors on your site longer, reducing bounce rates and increasing engagement.
4. Boosts Click-Through Rates (CTR)
Optimizing meta titles and descriptions with compelling language encourages users to click on your link in search results.
- A well-crafted title tag highlights the relevance of your page.
- A persuasive meta description gives users a reason to choose your page over competitors.
5. Supports Search Engine Crawling and Indexing
Search engines rely on On-Page SEO Techniques elements, like proper URL structure, headings, and internal links, to crawl and index your pages efficiently.
- Without on-page optimization, search engines may struggle to understand your content, leading to lower rankings.
- Proper optimization ensures every page on your site gets indexed correctly and stands a chance of ranking.
6. Drives Targeted Traffic and Leads to Higher Conversions
On-Page SEO Techniques aligns your content with the search intent of your audience.
- By optimizing for specific keywords, your pages attract users actively searching for what you offer.
- Targeted traffic is more likely to convert into leads, sales, or other desired actions.
7. Builds a Strong Foundation for Other SEO Efforts
On-page SEO works hand-in-hand with off-page and technical SEO.
- Without a solid on-page SEO foundation, off-page strategies like link building or social media marketing will be less effective.
- It ensures that any traffic driven to your site finds valuable and engaging content.
8. Adapts to Algorithm Updates
Search engines continually update their algorithms to prioritize high-quality content and user experience.
- By focusing on on-page SEO best practices, such as creating valuable content and optimizing for mobile, your site remains resilient to changes.
- This ensures long-term visibility and traffic.
9. Supports Branding and Authority Building:
On-page SEO helps establish your brand’s authority in your niche.
- High-quality content that is optimized and ranks well demonstrates your expertise and credibility.
- Users are more likely to trust a brand that consistently provides helpful and accessible information.
10. Cost-Effective and Sustainable Strategy:
Unlike paid ads, which require ongoing investment, the results of on-page SEO are long-lasting.
- Once optimized, a page can continue to attract traffic without additional costs.
- It provides a high return on investment (ROI) over time.
What Is The Difference Between SEO, Off-Page SEO and On-Page SEO?
SEO is a broad term encompassing all the strategies used to improve a website’s visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). On-page SEO and off-page SEO are two distinct subsets of SEO, each focusing on different aspects of optimization.
Key Differences Between On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO

| Aspect | On-Page SEO | Off-Page SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Internal website elements. | External factors outside the website. |
| Control | Fully within your control. | Requires third-party involvement (e.g., backlinks). |
| Activities | Content creation, keyword optimization, title tags, internal links, meta descriptions. | Link building, social media promotion, guest blogging, brand mentions. |
| Goal | Improve relevance and user experience. | Enhance authority and trustworthiness. |
| Tools Used | Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, SEMrush (on-page analysis). | Ahrefs, Moz, BuzzSumo (link and outreach tracking). |
| Time to See Results | Relatively quicker (weeks to months). | Slower, as it depends on external factors. |
15 On-Page SEO Techniques
On-Page SEO is a crucial aspect of digital marketing that focuses on optimizing individual web pages to improve search engine rankings, attract organic traffic, and enhance user experience. By implementing a variety of techniques, websites can ensure they are fully optimized for search engines and provide relevant, valuable content to visitors. These techniques involve optimizing elements like keywords, titles, meta descriptions, images, URLs, and page speed, along with creating high-quality content that meets user intent. Additionally, improving website navigation, mobile-friendliness, and user experience are also key components of On-Page SEO. In this competitive digital landscape, mastering these on-page strategies helps websites achieve higher visibility, better engagement, and improved conversions.
| No. | Technique | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Keyword Research | Identify target keywords with high search volume and relevance to optimize content effectively. |
| 2 | Title Tag Optimization | Create keyword-rich, compelling titles under 60 characters to improve rankings and CTR. |
| 3 | Meta Description | Write concise, keyword-focused descriptions under 160 characters to attract clicks. |
| 4 | Content Quality | Publish unique, informative, and engaging content that satisfies user intent. |
| 5 | Headings and Page Structure | Use structured headings (H1 for main title, H2/H3 for subheadings) with relevant keywords. |
| 6 | Internal Linking | Link to other pages on your site to improve navigation and pass link equity. |
| 7 | URL Structure | Use clean, descriptive URLs with keywords to make them search-engine-friendly. |
| 8 | Image Optimization | Compress images, use descriptive file names, and include alt tags with keywords. |
| 9 | Mobile Optimization | Ensure the website is mobile-friendly and responsive on all devices. |
| 10 | Page Speed | Optimize site loading times by compressing files, enabling caching, and reducing server response time. |
| 11 | Keyword Placement | Incorporate keywords naturally in the title, headings, first 100 words, and throughout the content. |
| 12 | Content Readability | Write content in simple, clear language, using bullet points and short paragraphs for readability. |
| 13 | Schema Markup | Implement structured data to enhance SERP features like rich snippets and FAQ sections. |
| 14 | Canonical Tags | Use canonical tags to avoid duplicate content issues and consolidate ranking signals. |
| 15 | User Experience (UX) | Focus on site design, navigation, and usability to engage users and reduce bounce rates. |
These techniques work together to improve search engine rankings, attract targeted traffic, and create a better user experience.
1. Keyword Research:
Keyword Research is the process of identifying and analyzing the terms and phrases that users are searching for on search engines, with the goal of targeting those keywords in your content. It is a crucial aspect of SEO because it helps you understand what topics your audience is interested in and ensures that your content is optimized to appear in relevant search results.
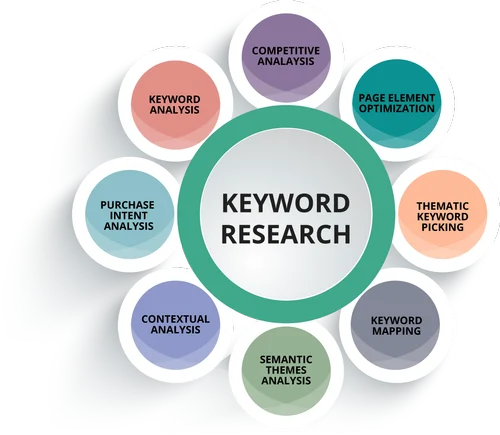
The key steps in keyword research typically include:
- Identifying Target Keywords: Discover the most relevant keywords that potential customers are using to search for products, services, or information related to your website.
- Analyzing Search Volume: Evaluate how often specific keywords are searched by users. This helps you prioritize high-volume keywords that will bring more traffic.
- Assessing Competition: Look at how competitive the keyword is. High-competition keywords may be harder to rank for, while long-tail keywords (more specific phrases) are usually easier to target.
- Understanding Search Intent: Determine the purpose behind a user’s search (e.g., informational, transactional, or navigational) to ensure your content aligns with what they are looking for.
- Selecting Keywords: Choose a mix of short-tail (broad) and long-tail (specific) keywords to optimize your website effectively, ensuring you can attract relevant traffic while minimizing competition.
Keyword research helps guide content creation, SEO strategy, and online marketing campaigns, ensuring that your website can rank for terms that are both relevant and valuable to your audience.
2. Title Tag Optimization:
Title Tag Optimization is the process of crafting a compelling and keyword-rich title for your web pages that accurately represents the content of the page and attracts both search engines and users. The title tag is an essential on-page SEO element because it appears as the clickable headline in search engine results pages (SERPs) and is one of the first things search engines look at to understand the content of a page.

Key Aspects of Title Tag Optimization:
- Keyword Integration: Include primary keywords that your target audience is likely to search for. However, ensure it reads naturally and isn’t overstuffed with keywords.
- Length: Keep the title tag under 60 characters, as search engines typically truncate longer titles in the SERPs. This helps ensure the entire title is visible to users.
- Branding: Include your brand name at the end of the title tag, especially for important pages or high-traffic keywords, to help increase brand recognition and trust.
- Clarity and Relevance: Make sure the title accurately reflects the page’s content. Misleading titles may increase bounce rates and negatively affect rankings.
- Engagement: Craft titles that are compelling and click-worthy, encouraging users to click on your page when they see it in the search results.
- Avoid Duplicate Titles: Each page on your website should have a unique title to avoid keyword cannibalization and improve the relevance of each page in search results.
By optimizing your title tags, you can improve your website’s visibility in search engines, drive more traffic, and enhance user engagement.
3. Optimize Meta Descriptions:
The page meta description is shown on the search engine results page (SERPS). It has to be descriptive, up to 200 characters, and unique for each page.
It’s your opportunity to advertise your page and convince users to click your link and visit your website rather than selecting one of the other links.
It should be noted that Google does not always show the custom meta description, but they often use an automated description if they believe it is more useful for the searcher.

The most important meta-description optimization tips are:
Avoid auto-generated descriptions – Even though Google may not use your description, it’s always a best practice to avoid using auto-generated descriptions that sometimes don’t make sense.
Add your target keyword(s) in the description – Google still highlights the search terms both in the title and description so adding your target keywords, makes descriptions more relevant and appealing to the searcher.
4. Content Quality:
One of the big SEO mistakes many publishers make is creating new content without going back to review and update their existing content. You should monitor your rankings and perform regular content updates as part of your on-page SEO audit. Content freshness is a known ranking factor.
- Twice (at least) per year, monitor your Google rankings to find your top-performing pages.
- Find for which keywords a page is ranking. You can use Google Search Console or your favorite SEO tool.
- Search on Google and analyze the content of the top-ranking pages for those keywords.
- Find missing topics/features included in the top pages and adjust your content accordingly.
- Refresh your visuals.
- Check your outbound and internal links.
- Ensure that your content matches the user intent.
- Optimize your content for Google features (featured and rich snippets).
5. Headings and Page Structure:
A page needs to be properly formatted. Think of it as a report which needs to have a heading (h1) and subheadings (h2, h3).
The H1 Tag:
Each page needs to have only one H1 tag. In all CMS, by default, the title of a page is wrapped into H1 tags.
You can either choose to have the same <title> and <h1> tag or provide an alternative title for the heading.
Remember that search engines display in the results what they find in the title tag, not the h1 tag. If you’re confused, read the differences between the two.

As far as the other headings are concerned (h2, h3), the things you need to have in mind are the following:
- Avoid using a single word for a heading, but make your headings interesting and useful for users who like to skim-read an article.
- Use headings hierarchically, i.e., the first heading tag is the <h1> and then the <h2> and then <h3>, <h4>, etc.
- The subheadings are a great place to use related keywords in your content.
6. Internal Linking:
Internal linking, i.e., linking to pages within your website, is a good SEO practice.
- It’s a way to let search engines know about your other pages.
- It’s a way to tell search engines your most important pages.
- It’s a way to increase the time users spend on your site.
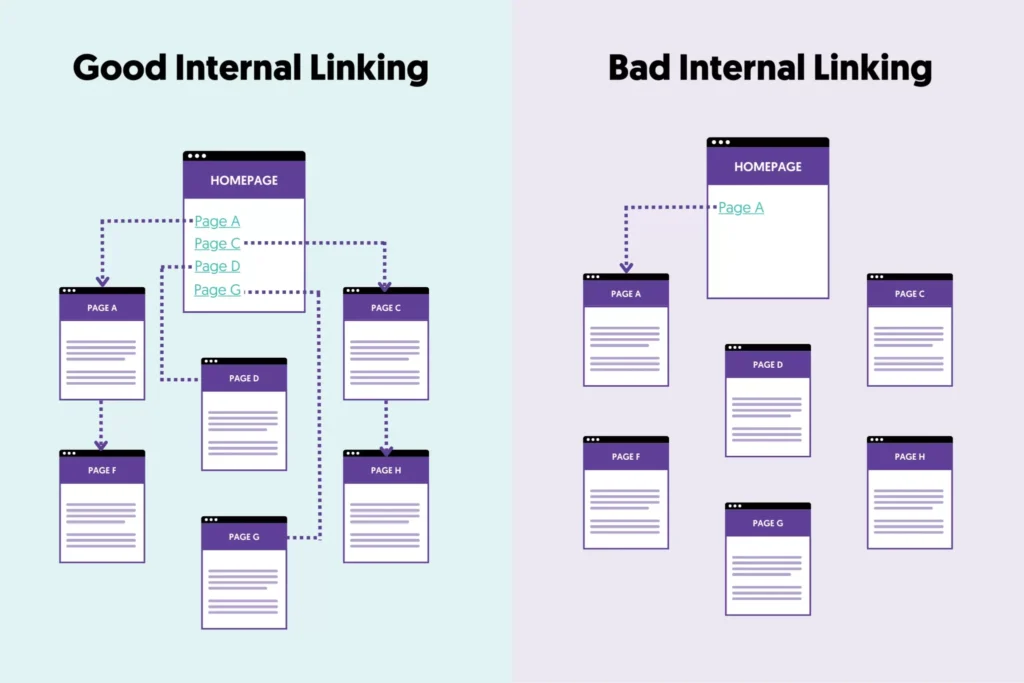
Best practices for internal linking:
- Add internal links when they are useful for your reader
- No more than 15 internal links per page (this is my opinion and not based on any research or studies)
- When possible, add the links in the main body of your webpage (not in the footer or sidebar)
- Link from older posts to newer posts and vice versa.
- The most important pages of your website should have a greater number of internal links.
- View the internal links report in Google Search Console to understand your internal linking structure.
7. URL Optimization:
Optimizing your URLs is important for maximum SEO. It has two parts. The first part is URL optimization and the second is the URL structure.
A permanent link (also known as a slug) is the unique URL of each page.
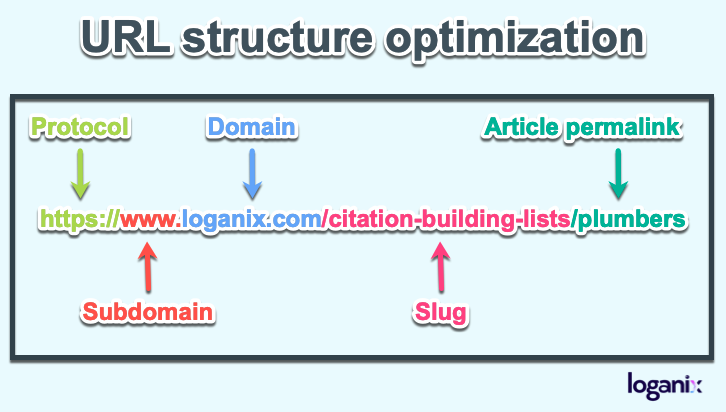
Good URLs should be less than 255 characters and use hyphens to ‘-‘ separate the different parts.
Just like the page title, an SEO-friendly URL is short, descriptive, and includes your target keyword.
Best practices for optimizing your URL structure:
- Create a matching site Structure and URL structure – The URL structure should mimic the actual structure of a website.
- Group related content into categories – Group your pages into categories to help users and search engines find what they want faster. It’s like having a warehouse with many uncategorized items versus a warehouse with all the items assigned to a dedicated category.
- Add a Breadcrumb menu– A breadcrumb is helpful because it allows users to navigate your website in a structured way since they always know where they are and how far from the home page.
8. Image Optimization:
Images are important for presentation purposes. They make a page more interesting and easier to understand.
The biggest problems with images are that search engines don’t understand them and that they add to the loading speed of a page.

Best practices for SEO optimizing images:
- Use original images. If you need to use an existing image from the web you need to reference the source.
- Optimize the size of the images – the smaller the size (in bytes) of the image the better.
- Use an ALT tag to describe the image – This helps search engines understand what the image is about.
- Use descriptive filenames – Don’t just name your image ‘image1.jpg’ but try to use descriptive filenames, for example, ‘man-doing-push-ups.jpg’.
- Use a Content Delivery Network – If you have a lot of images on a single page you can use a CDN service that will make your page load faster. In simple terms, your images will be hosted and served by a number of servers, and this speeds up the loading process.
9. Mobile optimization
Mobile optimization is the process of designing and adjusting a website or digital content to provide an optimal experience for users on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. It ensures that the content is accessible, visually appealing, and functional regardless of the screen size or device.
Key Aspects of Mobile Optimization:
1. Responsive Design: Ensures that the website layout adapts to different screen sizes and resolutions.
2. Fast Loading Times: Optimizing images, reducing code, and using caching techniques to improve loading speed on mobile networks.
3. Mobile-Friendly Navigation: Simplifying menus and buttons to accommodate touch gestures and smaller screens.
4. Readable Text: Ensuring font sizes and styles are legible without zooming.
5. Optimized Images and Videos: Compressing media files to reduce load times while maintaining quality.
6. Touch-Friendly Elements: Designing buttons and links large enough for easy tapping.
7. Eliminating Intrusive Pop-Ups: Avoiding pop-ups or interstitials that can hinder the mobile user experience.
8. AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages): Using lightweight versions of web pages to improve speed and usability on mobile devices.

Importance of Mobile Optimization:
Increased Mobile Traffic: With most users browsing the internet on mobile devices, mobile optimization ensures you don’t lose potential visitors.
Improved User Experience: A seamless mobile experience leads to higher engagement and reduced bounce rates.
Better SEO Performance: Search engines like Google prioritize mobile-optimized websites in search rankings, particularly with the mobile-first indexing approach.
Higher Conversion Rates: A mobile-friendly website encourages users to complete desired actions, such as making purchases or filling out forms.
Mobile optimization is essential for businesses to stay competitive in the digital landscape.
10. Page Speed:
Page speed refers to the amount of time it takes for a web page to fully load and become usable for visitors. It is a critical factor for user experience, search engine optimization (SEO), and overall website performance.
Key Metrics of Page Speed:
Page Load Time: The total time it takes to load all the content on a page.
Time to First Byte (TTFB): The time the browser waits to receive the first byte of data from the server.
First Contentful Paint (FCP): The time it takes to render the first visible content (text, image, etc.) on the screen.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): The time it takes to load the largest visible element (like a hero image or headline).
Time to Interactive (TTI): The time it takes for the page to become fully interactive for users.
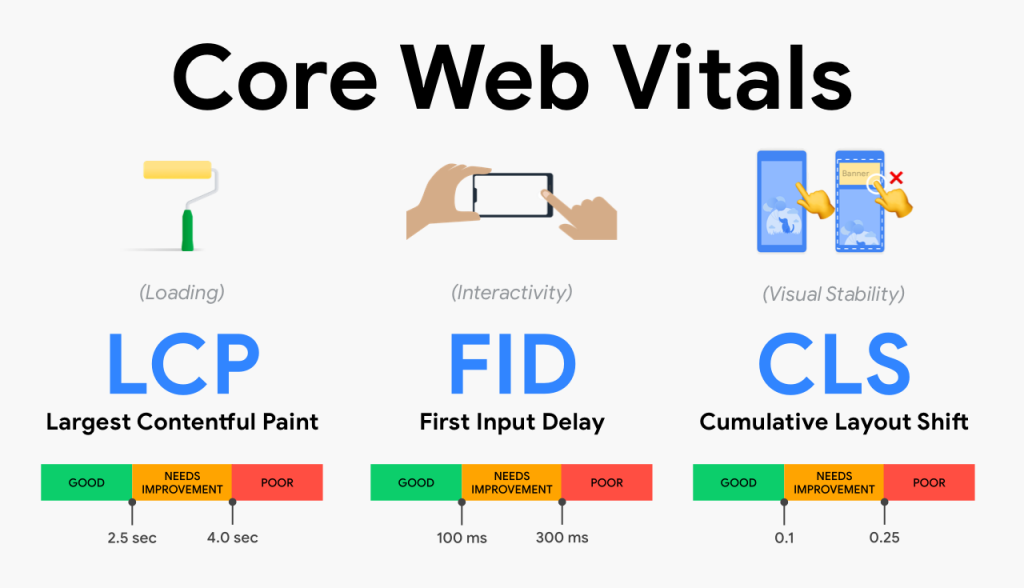
Why Page Speed is Important:
1.User Experience: Faster-loading pages provide a smoother browsing experience, reducing frustration and bounce rates.
2. SEO Benefits: Search engines like Google use page speed as a ranking factor. A faster site can rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs).
3. Conversion Rates: Studies show that faster websites lead to higher conversion rates, as users are less likely to abandon slow-loading pages.
4. Mobile Optimization: Page speed is especially crucial on mobile devices, where users may have slower connections.
How to Improve Page Speed:
- Optimize Images: Compress and resize images to reduce file size.
- Minify Code: Remove unnecessary characters, spaces, and comments from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Distribute content across multiple servers to deliver it faster to users worldwide.
- Enable Browser Caching: Allow users’ browsers to store static files for faster repeat visits.
- Use a Fast Hosting Provider: Choose a reliable hosting service with high performance.
- Lazy Loading: Load images and videos only when they are about to appear in the user’s viewport.
- Reduce Redirects: Minimize redirects to avoid additional load time.
Improving page speed benefits both users and search engine rankings, making it a priority for any website owner or digital marketer.
11. Keyword Placement:
Keyword placement is the strategic incorporation of target keywords into the content of a webpage to improve its visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). Proper keyword placement ensures that your content aligns with user search queries and satisfies search engine algorithms.
Key Areas for Keyword Placement:
Title Tag
- Place the primary keyword near the beginning of the title tag.
- Example: “Best Digital Marketing Services in Chennai”
Meta Description
- Include the primary keyword in the meta description to attract clicks from search engine users.
- Example: “Looking for top-notch digital marketing services in Chennai? We specialize in SEO, SMM, and SEM to grow your business.”
Headings (H1, H2, H3)
- Use keywords in the main heading (H1) and subheadings (H2, H3) to structure the content effectively.
- Example: H2: “Why Choose Digital Marketing Services in Chennai?”
Tips for Effective Keyword Placement:
- Prioritize Natural Flow: Avoid forcing keywords into sentences. Focus on readability and relevance.
- Use Variations: Include synonyms and long-tail keyword variations to target a broader audience.
- Optimize for Intent: Align keyword placement with user search intent (informational, navigational, or transactional).
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Overusing keywords can lead to penalties from search engines.
- Focus on Semantic SEO: Incorporate related terms and concepts to enhance context and relevance.
By placing keywords strategically and naturally, you can enhance your content’s ranking potential while maintaining a positive user experience.
12. Content Readability:
Content readability refers to how easily and effectively a reader can understand your text. It involves writing in a way that matches the target audience’s reading level, ensuring clarity, engagement, and retention. Readable content keeps users on the page longer and enhances user experience, directly impacting search engine optimization (SEO) and conversions.

Factors Affecting Content Readability:
- Sentence Length: Shorter sentences are easier to read and process.
- Word Choice: Simple, familiar words work better than jargon or technical terms for general audiences.
- Paragraph Structure: Short paragraphs with clear ideas improve readability.
- Text Formatting: Proper use of headings, bullet points, bold text, and white space helps organize content and make it scannable.
- Active Voice: Writing in an active voice is clearer and more direct than passive voice.
- Grammar and Punctuation: Proper grammar and punctuation eliminate confusion and maintain professionalism.
- Reading Level: Content should match the literacy level of the target audience, often assessed using readability scores like Flesch Reading Ease or Flesch-Kincaid.
Tips to Improve Content Readability:
- Write for Your Audience: Understand the demographics, interests, and reading level of your audience.
- Use Short Sentences and Paragraphs: Aim for sentences with 20 words or fewer and paragraphs with 2–3 sentences.
- Incorporate Subheadings: Break content into sections with descriptive headings (H2, H3).
- Utilize Bullet Points and Lists: Use lists to present information in a digestible format.
- Use Simple Language: Replace complex words with simpler alternatives.
- Example: Use “help” instead of “facilitate.”
- Add Visual Elements: Include images, infographics, and charts to complement the text.
- Engage the Reader: Ask questions, use a conversational tone, and speak directly to the reader.
- Avoid Overloading Information: Stick to one main idea per section to avoid overwhelming the reader.
- Test Across Devices: Ensure readability on both desktop and mobile platforms.
- Proofread and Edit: Review the content multiple times to remove errors and refine flow.
Benefits of Readable Content:
- Enhanced User Experience: Makes it easier for readers to engage with and understand the content.
- Increased Dwell Time: Readable content keeps users on your site longer.
- Better SEO: Search engines favor well-structured, easy-to-read content.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Clear and concise messaging drives action from readers.
Readable content is the cornerstone of effective communication and plays a significant role in achieving digital marketing success.
13. Schema Markup:
Schema markup (or structured data) is a standardized code format added to a website to help search engines understand the content better and display it more effectively in search results. It uses vocabulary developed by Schema.org and works across search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
By incorporating schema markup, you can enhance your search result listings with rich snippets, making them more informative and visually appealing to users.
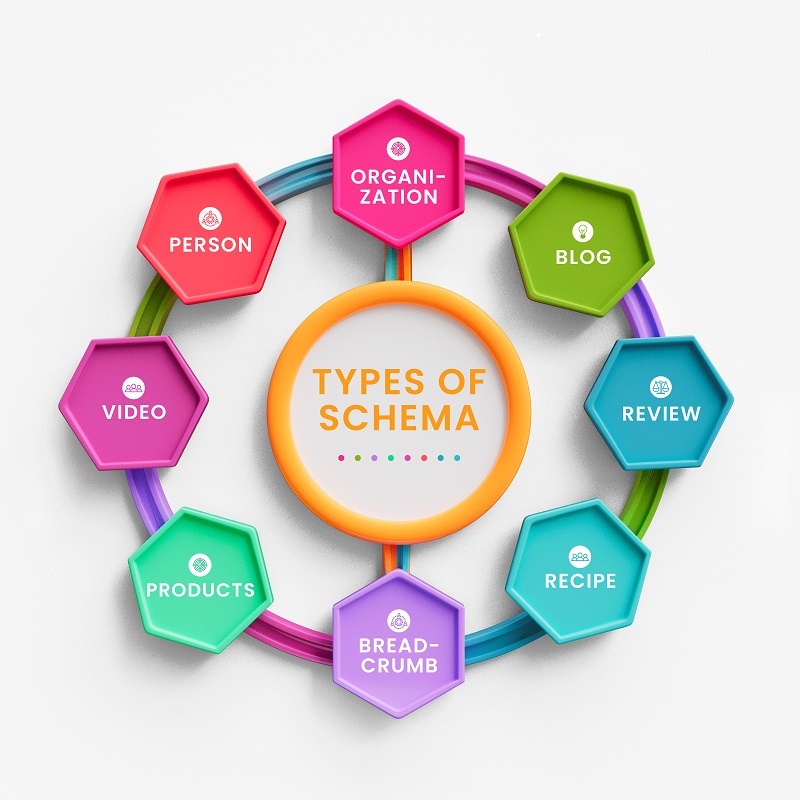
Types of Schema Markup:
Schema markup can be applied to various content types, such as:
- Articles: News or blog content.
- Events: Details about upcoming events, including date, time, and location.
- Products: Information about products, pricing, reviews, and availability.
- Organizations: Details about businesses, including name, logo, address, and contact information.
- Local Businesses: Data about local services, including operating hours and reviews.
- Person: Information about individuals, such as name, job title, and social media links.
- Recipes: Details about cooking instructions, ingredients, and preparation time.
- FAQs: Question-and-answer formats to display directly in search results.
- Reviews and Ratings: Star ratings or aggregate reviews for products or services.
- Breadcrumbs: Navigation path for users and search engines.
Schema Markup and SEO:
While schema markup itself doesn’t directly boost rankings, it improves:
- Search appearance (rich results attract more clicks).
- SERP real estate (occupies more space with detailed information).
- User experience (delivers relevant details upfront).
Implementing schema markup is a powerful way to enhance your website’s visibility and usability in search results, making it an essential tool in digital marketing strategies.
14. Canonical Tags:
Canonical tags (or rel="canonical") are HTML elements used to prevent duplicate content issues by specifying the preferred (canonical) version of a web page. They guide search engines to treat a specific URL as the authoritative source among multiple similar or identical pages, consolidating the ranking signals for better SEO performance.
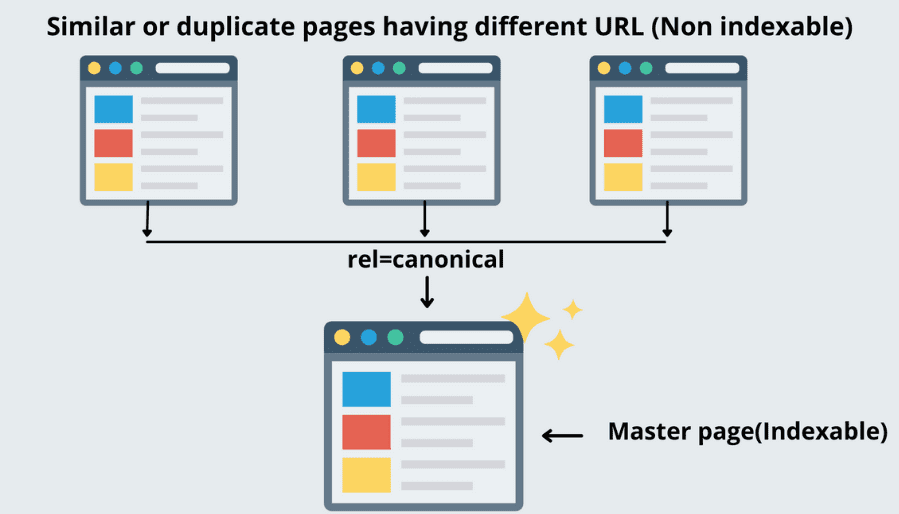
Why Canonical Tags Are Important:
Avoid Duplicate Content Issues: Helps search engines understand which page to prioritize if similar content exists across multiple URLs.
- Example:
https://example.com,https://www.example.com, andhttps://example.com/index.htmlmay lead to the same content but are treated as separate pages without a canonical tag.
Consolidate Ranking Signals: Combines link equity, page authority, and other SEO metrics from duplicate URLs to the canonical URL.Improved Crawl Efficiency: Prevents search engines from wasting crawl budget on duplicate pages.
Benefits of Canonical Tags:
Protects SEO Efforts: Ensures search engines focus on the right page, maximizing visibility.
Reduces Indexing Confusion: Prevents dilution of link equity across multiple pages.
Improves Search Rankings: Helps consolidate ranking signals and improves overall page authority.
Simplifies URL Management: Helps manage dynamic or parameterized URLs effectively.
Tools to Test Canonical Tags:
Google Search Console: Check which pages Google has indexed as canonical.
SEO Plugins: Plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math for WordPress automate canonical tag management.
Browser Inspect Tool: Use the browser’s developer tools to inspect the <head> section for canonical tags.
Third-Party Tools: Tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs can help identify and audit canonical tags.
Canonical tags are an essential part of technical SEO, helping to streamline your site’s indexing and ensure the correct pages receive visibility and authority.
15. User Experience (UX):
User Experience (UX) refers to the overall experience a user has while interacting with a product, service, or system, particularly in terms of how easy, enjoyable, and efficient it is to use. In the context of websites and digital products, UX focuses on creating intuitive, accessible, and satisfying experiences for users to achieve their goals effectively.
Key Elements of User Experience:
1. Usability: Ensures the product is easy to use, learn, and navigate.
- Example: A clean navigation bar on a website that helps users find what they’re looking for quickly.
2. Accessibility: Makes the product usable for people of all abilities, including those with disabilities.
- Example: Providing alt text for images and ensuring content is screen-reader friendly.
3. Aesthetics: Visual appeal and design elements that enhance the user’s interaction.
- Example: Using consistent colors, fonts, and layouts to make the interface visually pleasing.
Importance of UX:
- Enhances User Satisfaction: A good UX design makes interactions enjoyable and productive.
- Improves Retention: Positive experiences encourage users to return and engage further.
- Boosts Conversion Rates: Clear and intuitive interfaces drive users to take desired actions, like making a purchase or signing up.
- Strengthens Brand Loyalty: A seamless UX builds trust and a positive association with the brand.
- Supports SEO: Search engines prioritize user-friendly websites with lower bounce rates and higher engagement.
- Saves Costs: Identifying and addressing UX issues early reduces costly fixes and redesigns later.
Conclusion:
Mastering on-page SEO techniques is critical for improving search engine rankings, driving organic traffic, and delivering a better user experience. By implementing both basic and advanced strategies, you ensure that your website is optimized for both search engines and users.
By consistently applying these 15 techniques, your website can achieve higher rankings, attract more qualified traffic, and create lasting engagement. Remember, on-page SEO is an ongoing process—continual improvement is key to staying competitive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.

